15 KiB
Udp2raw-tunnel
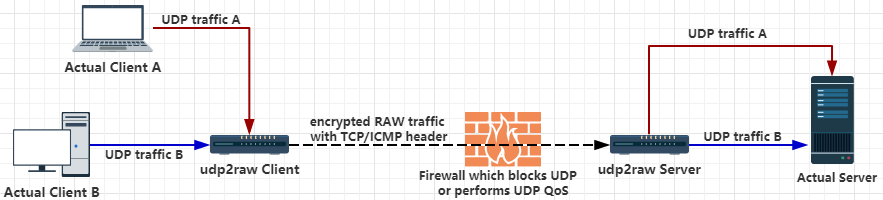
支持心跳保活、自动重连,重连后会恢复上次连接,在底层掉线的情况下可以保持上层不掉线。同时有加密、防重放攻击、信道复用的功能。
udp2raw+finalspeed step_by_step教程
提示:
udp2raw不是加速器,只是一个帮助你绕过UDP限制的工具。如果你需要UDP“加速器” (改善UDP丢包),请看UDPspeeder。
UDPspeeder的repo:
https://github.com/wangyu-/UDPspeeder
支持的平台
Linux主机,有root权限或cap_net_raw capability.。可以是PC、android手机/平板、openwrt路由器、树莓派。主机上最好安装了iptables命令(apt/yum很容易安装)。
Release中提供了amd64、x86、arm、mips_be、mips_le的预编译binary.
对于windows和mac用户:
可以用这个repo里的udp2raw。
对于ios和游戏主机用户:
可以把udp2raw运行在局域网的其他机器/虚拟机上。最好的办法是买个能刷OpenWrt/LEDE/梅林的路由器,把udp2raw运行在路由器上。
功能特性
把udp流量伪装成tcp /icmp
用raw socket给udp包加上tcp/icmp包头,可以突破udp流量限制或Udp QOS。或者在udp nat有问题的环境下,提升稳定性。 另外也支持用raw 发udp包,这样流量不会被伪装,只会被加密。
模拟TCP3次握手
模拟TCP3次握手,模拟seq ack过程。另外还模拟了一些tcp option:MSS,sackOk,TS,TS_ack,wscale,用来使流量看起来更像是由普通的linux tcp协议栈发送的。
心跳保活、自动重连,连接恢复
心跳保活、自动重连,udp2raw重连可以恢复上次的连接,重连后上层连接继续有效,底层掉线上层不掉线。有效解决上层连接断开的问题。 (功能借鉴自kcptun-raw)(就算你拔掉网线重插,或者重新拨号获得新ip,上层应用也不会断线)
加密、防重放攻击
用aes128cbc加密(或更弱的xor),hmac-sha1(或更弱的md5/crc32/simple)做数据完整校验。用类似ipsec/openvpn的replay window机制来防止重放攻击。
其他特性
信道复用,client的udp端支持多个连接。
server支持多个client,也能正确处理多个连接的重连和连接恢复。
NAT 穿透 ,tcp icmp udp模式都支持nat穿透。
支持Openvz,配合finalspeed使用,可以在openvz上用tcp模式的finalspeed.
支持Openwrt,没有编译依赖,容易编译到任何平台上。
关键词
突破udp qos,突破udp屏蔽,openvpn tcp over tcp problem,openvpn over icmp,udp to icmp tunnel,udp to tcp tunnel,udp via icmp,udp via tcp
简明操作说明
安装
下载编译好的二进制文件,解压到任意目录。
https://github.com/wangyu-/udp2raw-tunnel/releases
运行
假设你有一个server,ip为44.55.66.77,有一个服务监听在udp 7777端口。 假设你本地的主机到44.55.66.77的UDP流量被屏蔽了,或者被qos了
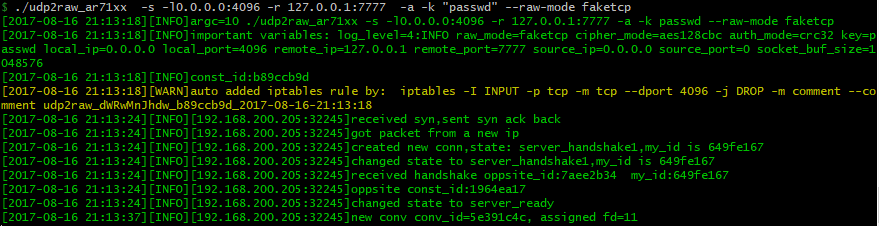
在server端运行:
./udp2raw_amd64 -s -l0.0.0.0:4096 -r127.0.0.1:7777 -k "passwd" --raw-mode faketcp --cipher-mode xor -a
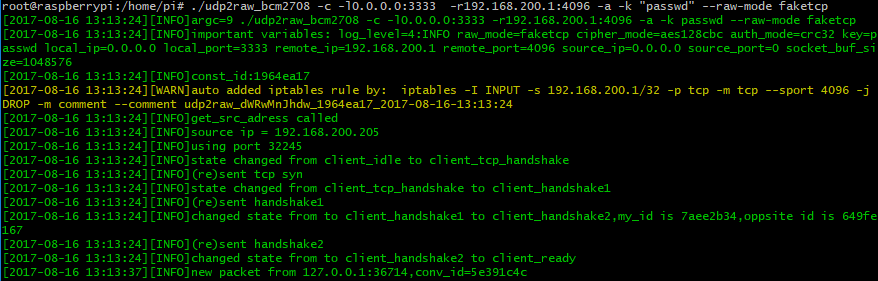
在client端运行:
./udp2raw_amd64 -c -l0.0.0.0:3333 -r44.55.66.77:4096 -k "passwd" --raw-mode faketcp --cipher-mode xor -a
(以上例子需要用root账号运行。 用非root运行udp2raw需要一些额外的步骤,具体方法请看 这个 链接。用非root运行更安全)
Server端输出:
Client端输出:
现在client和server之间建立起了,tunnel。想要在本地连接44.55.66.77:7777,只需要连接 127.0.0.1:3333。来回的所有的udp流量会被经过tunneling发送。在外界看起来是tcp流量,不会有udp流量暴露到公网。
MTU设置(重要)
不论你用udp2raw来加速kcptun还是vpn,为了稳定使用,都需要设置合理的MTU(在kcptun/vpn里设置,而不是在udp2raw里),建议把MTU设置成1200。client和server端都要设置。
提醒
--cipher-mode xor表示仅使用简单的XOR加密,这样可以节省CPU占用,以免CPU成为速度瓶颈。如果你需要更强的加密,可以去掉此选项,使用默认的AES加密。加密相关的选项见后文的--cipher-mode和--auth-mode。
如果要在anroid上运行,请看Android简明教程
-a选项会自动添加一条/几条iptables规则,udp2raw必须和相应的iptables规则配合才能稳定工作,一定要注意不要忘了-a(这是个常见错误)。 如果你不想让udp2raw自动添加iptables规则,可以自己手动添加相应的iptables规则(看一下-g选项),然后以不带-a的方式运行udp2raw。
进阶操作说明
命令选项
udp2raw-tunnel
git version:6e1df4b39f build date:Oct 24 2017 09:21:15
repository: https://github.com/wangyu-/udp2raw-tunnel
usage:
run as client : ./this_program -c -l local_listen_ip:local_port -r server_address:server_port [options]
run as server : ./this_program -s -l server_listen_ip:server_port -r remote_address:remote_port [options]
common options,these options must be same on both side:
--raw-mode <string> available values:faketcp(default),udp,icmp
-k,--key <string> password to gen symetric key,default:"secret key"
--cipher-mode <string> available values:aes128cbc(default),xor,none
--auth-mode <string> available values:hmac_sha1,md5(default),crc32,simple,none
-a,--auto-rule auto add (and delete) iptables rule
-g,--gen-rule generate iptables rule then exit,so that you can copy and
add it manually.overrides -a
--disable-anti-replay disable anti-replay,not suggested
client options:
--source-ip <ip> force source-ip for raw socket
--source-port <port> force source-port for raw socket,tcp/udp only
this option disables port changing while re-connecting
other options:
--conf-file <string> read options from a configuration file instead of command line.
check example.conf in repo for format
--fifo <string> use a fifo(named pipe) for sending commands to the running program,
check readme.md in repository for supported commands.
--log-level <number> 0:never 1:fatal 2:error 3:warn
4:info (default) 5:debug 6:trace
--log-position enable file name,function name,line number in log
--disable-color disable log color
--disable-bpf disable the kernel space filter,most time its not necessary
unless you suspect there is a bug
--sock-buf <number> buf size for socket,>=10 and <=10240,unit:kbyte,default:1024
--force-sock-buf bypass system limitation while setting sock-buf
--seq-mode <number> seq increase mode for faketcp:
0:static header,do not increase seq and ack_seq
1:increase seq for every packet,simply ack last seq
2:increase seq randomly, about every 3 packets,simply ack last seq
3:simulate an almost real seq/ack procedure(default)
4:similiar to 3,but do not consider TCP Option Window_Scale,
maybe useful when firewall doesnt support TCP Option
--lower-level <string> send packets at OSI level 2, format:'if_name#dest_mac_adress'
ie:'eth0#00:23:45:67:89:b9'.or try '--lower-level auto' to obtain
the parameter automatically,specify it manually if 'auto' failed
--gen-add generate iptables rule and add it permanently,then exit.overrides -g
--keep-rule monitor iptables and auto re-add if necessary.implys -a
--clear clear any iptables rules added by this program.overrides everything
-h,--help print this help message
iptables 规则,-a和-g
用raw收发tcp包本质上绕过了linux内核的tcp协议栈。linux碰到raw socket发来的包会不认识,如果一直收到不认识的包,会回复大量RST,造成不稳定或性能问题。所以强烈建议添加iptables规则屏蔽Linux内核的对指定端口的处理。用-a选项,udp2raw会在启动的时候自动帮你加上Iptables规则,退出的时候再自动删掉。如果长期使用,可以用-g选项来生成相应的Iptables规则再自己手动添加,这样规则不会在udp2raw退出时被删掉,可以避免停掉udp2raw后内核向对端回复RST。
用raw收发udp包也类似,只是内核回复的是icmp unreachable。而用raw 收发icmp,内核会自动回复icmp echo。都需要相应的iptables规则。
--cipher-mode 和 --auth-mode
如果要最大的安全性建议用aes128cbc+hmac_sha1。如果要运行在路由器上,建议用xor+simple,可以节省CPU。但是注意xor+simple只能骗过防火墙的包检测,不能防止真正的攻击者。
--seq-mode
faketcp模式并没有模拟tcp的全部。所以理论上有办法把faketcp和真正的tcp流量区分开来(虽然大部分ISP不太可能做这种程度的包检测)。seq-mode可以改变一些seq ack的行为。如果遇到了连接问题,可以尝试更改。在我这边的移动线路用3种模式都没问题。
--keep-rule
定期主动检查iptables,如果udp2raw添加的iptables规则丢了,就重新添加。在一些iptables可能会被其他程序清空的情况下(比如梅林固件和openwrt的路由器)格外有用。
--fifo
指定一个fifo(named pipe)来向运行中的程序发送命令,例如--fifo fifo.file:
在client端,可以用echo reconnect >fifo.file来强制client换端口重连(上层不断线).对Server,目前没有效果。
--lower-level
大部分udp2raw不能连通的情况都是设置了不兼容的iptables造成的。--lower-level选项允许绕过本地iptables。在一些iptables不好改动的情况下尤其有效(比如你用的是梅林固件,iptables全是固件自己生成的)。
格式
if_name#dest_mac_adress,例如 eth0#00:23:45:67:89:b9 。eth0换成你的出口网卡名。00:23:45:67:89:b9换成网关的mac地址(如果client和server在同一个局域网内,可能不需要网关,这时候直接用对方主机的mac地址,这个属于罕见的应用场景,可以忽略)。
可以用--lower-level auto自动获取参数,如果获取参数失败,再手动填写。
client端获得--lower-level参数的办法
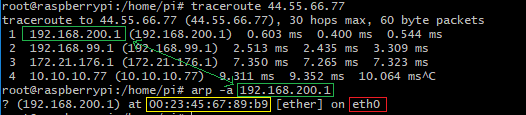
在client 端,运行traceroute <server_ip>,记下第一跳的地址,这个就是网关ip。再运行arp -s <网关ip>,可以同时查到出口网卡名和mac。
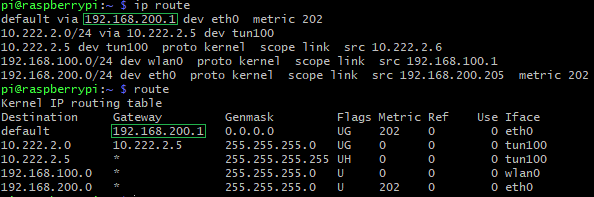
如果traceroute第一跳结果是* * *,说明网关屏蔽了对traceroute的应答。需要用ip route或route查询网关:
server端获得--lower-level参数的办法
如果client有公网ip,就traceroute <client_ip>。下一步和client端的方法一样。
如果client没有公网ip,就traceroute google.com 或traceroute baidu.com。下一步和client端的方法一样。
server端也可以用--lower-level auto 来尝试自动获得参数,如果无法连接再手动填写。
注意
如果用了--lower-level选项。server虽然还可以bind在0.0.0.0,但是因为你显式指定了网络接口,就只能工作在这一个网络接口了。
如果arps -s命令查询不到,首先再试几次。如果还是查询不到,那么可能是因为你用的是pppoe方式的拨号宽带,查询不到是正常的。这种情况下if_name填pppoe产生的虚拟interface,通常名字叫pppXXXX,从ifconfig命令的输出里找一下;des_mac_adress填00:00:00:00:00:00,例如ppp0#00:00:00:00:00:00
--conf-file
为了避免将密码等私密信息暴露给ps命令,你也可以使用 配置文件 来存储参数。
比如,将以上服务端参数改写成配置文件
server.conf:
-s
# 你可以像这样添加注释
# 注意,只有整行注释才能在配置文件里使用
# 注释必须独占一行
-l 0.0.0.0:4096
-r 127.0.0.1:7777
-a
-k passwd
--raw-mode faketcp
注意,当写入配置文件的时候,密码等参数两边的引号必须去除。
然后就可以使用下面的方式启动服务端
./udp2raw_amd64 --conf-file server.conf
性能测试
iperf3 的UDP模式有BUG,所以,这里用iperf3的tcp模式,配合Openvpn,测试udp2raw的性能。(iperf3 udp issue ,https://github.com/esnet/iperf/issues/296 )
openvpn关掉了自带的加密。
iperf3 命令:
iperf3 -c 10.222.2.1 -P40
iperf3 -c 10.222.2.1 -P40 -R
client主机
vultr 2.5美元每月套餐(single core 2.4ghz cpu,512m ram,日本东京机房),
server主机
bandwagonhost 3.99美元每年套餐(single core 2.0ghz cpu,128m ram,美国洛杉矶机房)
测试1
raw_mode: faketcp cipher_mode: xor auth_mode: simple
(反向的速度几乎一样,所以只发正向测试的图)
测试中cpu被打满。其中有30%的cpu是被openvpn占的。 如果不用Openvpn中转,实际达到100+Mb/S 应该没问题。
测试2
raw_mode: faketcp cipher_mode: aes128cbc auth_mode: md5
(反向的速度几乎一样,所以只发正向测试的图)
测试中cpu被打满。绝大多数cpu都是被udp2raw占用的(主要消耗在aes加密)。即使不用Openvpn,速度也不会快很多了。
应用
中转 kcptun
中转 finalspeed
udp2raw+finalspeed step_by_step教程
wiki
更多内容请看 wiki: